Quick Links: Table of Contents
- How Long Chesapeake Bay Retrievers Live. Chesapeake Bay Retriever Life Expectancy
- Lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever Compared to Other Dog Breeds
- Common Causes of Death in Chesapeake Bay Retriever, and how to Prevent Them.
- How To Prevent Genetic Problems in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
- How Old is Your Chesapeake Bay Retriever in Human Years
- How Long Do Chesapeake Bay Retrievers Live in Human Years?
- More Ways to Make Your Chesapeake Bay Retriever Live Long
- Conclusion on Chesapeake Bay Retriever Life Expectancy
How Long Chesapeake Bay Retrievers Live. Chesapeake Bay Retriever Life Expectancy
Generally, the lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever is from 10 to 12 years.
Moreover, a few years back, British Veterinarinan researchers performed a scientific study to determine the lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever. In this study, the scientists collected data on how long 45 pet Chesapeake Bay Retrievers lived.
From the study, it was found that Chesapeake Bay Retrievers have a average lifespan of 10.7 years. Furthermore, the study found that Chesapeake Bay Retrievers can live for as long as 15.6 years.
Furthermore, researchers from the University of Georgia conducted a study to find out what are the top causes of death in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers.
According to the study, the top 5 causes of death in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are:
- Neoplastic Disease: Issues involving tumors
- Hematopoietic Disease: Problems having to do with platelets, blood vessels, or clotting factors.
- Neurologic Disease: Refers to problems with the brain, nerves, and spinal cord.
- Trauma: Issues involving injury
- Musculoskeletal Disease: Refers to any problems with bones or muscles
In this article, we will explain each of these diseases and discuss how to prevent the early occurence of each in your Chesapeake Bay Retriever to make your Chesapeake Bay Retriever live a longer.
Also, in this article, we will discuss other things you can do to ensure that your Chesapeake Bay Retriever have a longer than average lifespan.
Do you want to know how old your Chesapeake Bay Retriever is in human years? Then, check out our Chesapeake Bay Retriever age to human years calculator
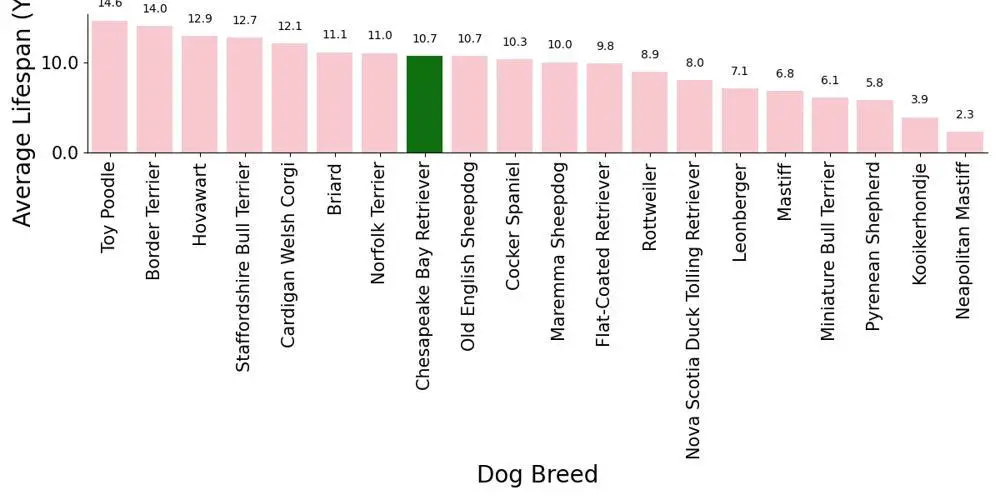
Lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever Compared to Other Dog Breeds
See in the table below how the lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever compares to the lifespan of other dog breeds.
| Dog Breed | Average Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|
| Toy Poodle Lifespan | 14.60 |
| Border Terrier Lifespan | 14.00 |
| Hovawart Lifespan | 12.90 |
| Staffordshire Bull Terrier Lifespan | 12.70 |
| Cardigan Welsh Corgi Lifespan | 12.10 |
| Briard Lifespan | 11.10 |
| Norfolk Terrier Lifespan | 11.00 |
| Chesapeake Bay Retriever Lifespan | 10.70 |
| Old English Sheepdog Lifespan | 10.70 |
| Cocker Spaniel Lifespan | 10.30 |
| Maremma Sheepdog Lifespan | 10.00 |
| Flat-Coated Retriever Lifespan | 9.83 |
| Rottweiler Lifespan | 8.92 |
| Nova Scotia Duck Tolling Retriever Lifespan | 8.00 |
| Leonberger Lifespan | 7.08 |
| Mastiff Lifespan | 6.83 |
| Miniature Bull Terrier Lifespan | 6.08 |
| Pyrenean Shepherd Lifespan | 5.79 |
| Kooikerhondje Lifespan | 3.92 |
| Neapolitan Mastiff Lifespan | 2.33 |

Common Causes of Death in Chesapeake Bay Retriever, and how to Prevent Them.
We will now discuss the common causes of death in Chesapeake Bay Retriever, according to scientific research. Also we will provide you advice on how to prevent these problems in your Chesapeake Bay Retriever.
Here are the causes of death, starting from the most common cause
-
Neoplastic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Neoplasms, or tumors, can be benign (like a lipoma), or malignant (cancer).
Neoplastic Disease is responsible for 28.5 percent of all deaths in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers.
Causes of Neoplastic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retriever
Neoplasms in dogs, just like in people, are caused by either a genetic predisposition (like some breast cancers), an environmental factor (like smoking in humans), or a combination of both.
How to Prevent Neoplastic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Just like in humans, there is little you can do to prevent cancers that are caused by genetic factors. You can, however, reduce the environmental risks that are associated with cancer. The `environmental` causes of neoplasia are chemical agents, infectious agents, and physical agents. An example of a chemical agent that could cause cancer in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers (and humans) is asbestos. An example of an infectious agent that could cause cancer in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers is the virus called canine adenovirus. An example of a physical agent that can cause cancer in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers is UV radiation from the sun, just like in humans.
Another way to prevent neoplasms in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers is to vaccinate them against harmful viruses, such as canine adenovirus (DHPP vaccine at 8 and 12 weeks and then once a year, every year). As in humans, early diagnosis is the key to supporting Chesapeake Bay Retrievers with neoplasms, so talk to your veterinarian if you find any new lumps, bumps, or discoloration on your Chesapeake Bay Retriever. You should also talk to your veterinarian if your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s gums look pale.
-
Hematopoietic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Normally, the body can regulate its own blood pressure and fluid volume without outside help. However, issues in hematopoesis can cause high or low blood pressure, blood clots, edema (fluid where it`s not supposed to be, like in the lungs), and even shock.
Hematopoietic Disease is responsible for 17.2 percent of all deaths in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers.
Causes of Hematopoietic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retriever
The causes of hematopoietic problems usually involve inflammation and immune responses gone wrong. This can cause congestion, hemorrhage, and many more problems.
How to Prevent Hematopoietic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Talk to your veterinarian if your dog`s gums or skin look very pale or very red. It`s also a good idea to talk to your vet if your dog is experiencing exercise intolerance. Many parasites can cause internal bleeding, so you should have your dog on flea, tick, and heartworm preventatives all year round. Here is a good flea and tick prevention medication (buy the box associated with your pet`s weight!).
-
Neurologic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
These problems include canine cognitive disfunction, dementia, stroke, Lyme disease, and more.
Neurologic Disease is responsible for 14.5 percent of all deaths in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers.
Causes of Neurologic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retriever
Neurological issues can be caused by vascular disease, inflammatory disease, infectious disease, metabolic disease, cancer, and developmental disorders.
How to Prevent Neurologic Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Some neurological problems can be caused by infectious agents, like Lyme disease. You should always get your dog vaccinated with the course recommended by your veterinarian.
-
Trauma in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
These includes cuts, bites, bruises, broken bones, wounds, scratches, and more.
Trauma is responsible for 12.9 percent of all deaths in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers.
Causes of Trauma in Chesapeake Bay Retriever
One of the most common causes of trauma in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers is getting hit by cats. Another common cause is bites and scratches from fighting or play with other dogs.
How to Prevent Trauma in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
The best way to keep your Chesapeake Bay Retriever from getting hit by a car is by having them on a fixed leash. Veterinarians do not recommend retractable leashes for dogs. This is because, oftentimes, dogs on retractable leashes will bolt into the road before their owners can lock the leash and get hit by cars, even though they were technically on a leash. Having a normal, fixed leash is also a good way to prevent your Chesapeake Bay Retriever from bolting on walks and getting into fights with other dogs before you can lock the leash.
Here is a good fixed leash that can save your Chesapeake Bay Retriever from traumatic accidents.
-
Musculoskeletal Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Musculoskeletal diseases are the common problems associated with bones and muscles. These include arthritis, vertebral issues, loss of skeletal muscle mass, hip dysplasia, trauma and breakages, and more.
Musculoskeletal Disease is responsible for 11.8 percent of all deaths in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers.
Causes of Musculoskeletal Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retriever
The causes of many musculoskeletal issues have to do with age, breed, and weight. Older Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are more prone to musculoskeletal issues, as are large breed dogs, and overweight dogs. Just like people, Chesapeake Bay Retrievers can get arthritis and other joint-related issues as they get older. Large-breed dogs tend to be prone to a condition called hip dysplasia, which essentially means that their hip joints degrade and get very painful. Overweight dogs tend to put more pressure on their joints, which can cause unnecessary wear and tear as well as serious damage to tendons and ligaments.
How to Prevent Musculoskeletal Disease in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
One way that you can help improve your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s musculoskeletal health (especially if they are old is by giving your Chesapeake Bay Retriever joint supplements like this one. You can also help prevent hip dysplasia and slipped discs by not allowing your Chesapeake Bay Retriever to jump too much, even if they are a puppy. Consider buying young Chesapeake Bay Retrievers a box or stool like this to help them get on the couch or bed, instead of letting them jump all the way from the ground. The most important way that you can keep your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s muscles and bones healthy is by not letting them get overweight. You should avoid letting your Chesapeake Bay Retriever eat table scraps and make sure that they get plenty of exercise. If your Chesapeake Bay Retriever is overweight and you know that you are strict with their diet and exercise, you should talk to your vet; they might have hypothyroidism, which is very common. If your Chesapeake Bay Retriever is overweight and you think you should try managing their diet a little more closely, you can start your Chesapeake Bay Retriever on a weight-management diet like this to help them get back to a healthier body condition.

How To Prevent Genetic Problems in Chesapeake Bay Retrievers
Every dog breed has a set of genetic problems to which it is predisposed, and the Chesapeake Bay Retriever is not an exception.
These disease will reduce your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s qualilty of life. Also, these diseases can shorten your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s lifespan.
The good news is that these diseases can be prevented in Chesapeake Bay Retriever offsprings by only breeding Chesapeake Bay Retriever that have been screened and cleared of genetic defects.
The Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA) is one the organizations that keep records of which disease to which a dog breed is genetically prone.
The OFA provides breeders recommendations on which genetic diseases that breeders should screen their dog parents and puppies for.
If you want a Chesapeake Bay Retriever puppy that will grow up to be healthy and live long, make sure that your Chesapeake Bay Retriever breeder screens your puppy or your puppy`s parents for the health problems that the OFA recommends for your puppy`s breed. This will increase the chances that your puppy is free from genetic defects.
If you do not know if your Chesapeake Bay Retriever has been screened for genetic health problems, then your can use an at-home genetic screening kit like this one to check your Chesapeake Bay Retriever for genetic health problems at home. This might help you in deciding whether to get your Chesapeake Bay Retriever a pet health insurance.
The following are the health tests that Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA) recommends that breeders should screen Chesapeake Bay Retrievers for:

How Old is Your Chesapeake Bay Retriever in Human Years
The table below shows your human years equivalent age of your Chesapeake Bay Retriever. This table is based on a dog-to-human age study conducted by researchers from Purdue University.
Learn more about how old your Chesapeake Bay Retriever is in human years here.
In 1997, researchers from Purdue University developed a method for converting a dog`s age to its human age. Their method was based on the 1953 work of the French Veterinarian, A. Lebeau that we discussed above.
Researchers from Purdue University took Lebeau`s work further by taking into account two important factors to develop a more accurate method for converting a dog`s age into its human equivalent age:
- The size of the dog: Smaller dog breeds live longer than larger breed dogs
- The lifespan of the dog: Dog breeds that live longer lives will age slower than dog breeds that live shorter lives
The average lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever is 10.7 years.
Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are medium-sized dogs. Chesapeake Bay Retrievers weigh 55 to 80 pounds.
The method developed by the Purdue University veterinarian researchers took into account the lifespan and size of Chesapeake Bay Retriever in converting Chesapeake Bay Retriever age to human age.
The researchers used data on the lifespan and weight of 5,608 mixed breed dogs and 17,927 purebred dogs to develop their method for converting the ages of dogs (of different breed sizes and lifespans ) to their equivalent human ages.
The calculator below lets you convert your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s age to its human age based on the Purdue University method. Just enter your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s age in the calculator and it will compute your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s human age. If you do not know your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s exact age, enter an approximate age in the calculator.
Also, the table below shows how old your Chesapeake Bay Retriever is in human years based on the method developed by the researchers.
Note that your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s human age changes day by day. Therefore, always check back to use the calculator to find your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s up-to-date human age.
Chesapeake Bay Retriever Age to Human Age Calculator (Purdue Uni. Method)
Below is a Chesapeake Bay Retriever age to human age calculator that is based on the methods developed by researchers from Purdue University.
The calculator will tell your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s human age based on your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s dog birthday. Also, the calculator will tell you which day is your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s human birthday! Try it out!
| Chesapeake Bay Retriever Age (Years) | Human Age (Years) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 14 |
| 2 | 21 |
| 3 | 26 |
| 4 | 32 |
| 5 | 37 |
| 6 | 42 |
| 7 | 46 |
| 8 | 50 |
| 9 | 54 |
| 10 | 58 |
| 11 | 62 |
| 12 | 66 |
| 13 | 71 |
| 14 | 75 |
| 15 | 80 |
| 16 | 85 |
How Long Do Chesapeake Bay Retrievers Live in Human Years?
The average lifespan of the Chesapeake Bay Retriever is 10.7 years. In human years, the Chesapeake Bay Retriever lives for 61 years.
How Old is 4-year-old Chesapeake Bay Retriever in Human Years?
A 4-year old Chesapeake Bay Retriever is 32 years old in human years.

How Old is 6-year-old Chesapeake Bay Retriever in Human Years?
A 6-year old Chesapeake Bay Retriever is 42 years old in human years.

How Old is 8-year-old Chesapeake Bay Retriever in Human Years?
A 8-year old Chesapeake Bay Retriever is 50 years old in human years.

How Old is 9-year-old Chesapeake Bay Retriever in Human Years?
A 9-year old Chesapeake Bay Retriever is 54 years old in human years.

More Ways to Make Your Chesapeake Bay Retriever Live Long
Here are more things your can do to make sure your Chesapeake Bay Retriever live a long life:
-
Regular Exercise: Research studies have shown that one of the very effective ways to make a dog live long is to ensure that a dog is in good shape. Adequate exercise will make your Chesapeake Bay Retriever fit and make it live longer.
-
Good Diet: A poorly-fed, underweight Chesapeake Bay Retriever does not have a good chance of living a long life. Similarly, an overweight Chesapeake Bay Retriever will have a shorter lifespan than a Chesapeake Bay Retriever that is of normal weight. Therefore, it is important that your feed your Chesapeake Bay Retriever high-quality dog food without overfeeding your Chesapeake Bay Retriever. Check out our Chesapeake Bay Retriever feeding guide here. Learn how you can prevent your Chesapeake Bay Retriever from being overweight here.
-
Proper Hydration: Water is essential for your Chesapeake Bay Retriever existence. Therefore, you should make sure your Chesapeake Bay Retriever has access to clean water whenever your Chesapeake Bay Retriever needs water. However, too much water is bad for your Chesapeake Bay Retriever. See our Chesapeake Bay Retriever water drinking guide to learn more on how to properly hydrate your Chesapeake Bay Retriever.
-
Spaying/Neutering: Sterilizing your Chesapeake Bay Retriever might prolong its life. Check out this guideline to know when it is the best time to spay/neuter your Chesapeake Bay Retriever.
-
Routine Vet Care: Regular preventative visits to the vet can help catch diseases early.
-
Vaccinations: Always make sure your Chesapeake Bay Retriever is up to date on its vaccination.
-
Dental Hygiene: Your Chesapeake Bay Retriever’s teeth can get infected, and if the infection goes unnoticed, that infection can spread to other parts of the body and become systemic. This could lead to a shortened lifespan. You must have your Chesapeake Bay Retriever teeth cleaned professionally at your vet’s office a couple of times in its lifetime. Talk with your vet about the best ages to have these cleanings done.
Conclusion on Chesapeake Bay Retriever Life Expectancy
We hope the information we have provided will help your in increasing your Chesapeake Bay Retriever`s life expectancy.
Tate Ackerman contributed to this article. Tate is a second-year veterinary student at Kansas State University. Tate is also a concurrent Ph.D. student. She has a lot of experience reading scientific literature and communicating that information to a non-veterinary audience. Tate was a veterinary technician for a companion animal practice before she applied to veterinary school.